Argument 사용법 - Run configurations -> Argument 값 대입

package day0117;
/**
* main method의 arguments 입력받기
*/
public class MainArguments {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(args[0]);
System.out.println(args[1]);
System.out.println(args[2]);
System.out.println(args[3]);
System.out.println(args[0]+args[1]);
//문자열은 +연산자만 사용할 수 있는데 붙임 연산을 수행
//문자열을 숫자로 변환
// int num=args[0]; //참조형(Sring -주소)을 기본형(int -값)에 할당할 수 없다.
// int num=(int)args[0]; //참조형(Sring -주소)을 기본형(int -값)으로 강제 형변환 될 수 없다.
//Wrapper class를 사용하여 문자열을 분석하여 정수로 변환하여 반환하는 일을 하는 method 사용
int num1=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int num2=Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.out.println(num1+" + "+ num2 + " = " + (num1+num2));
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
0
1
2
3
01
0 + 1 = 1
*제어문 ( Control Statement)
- 프로그램의 순차적인 흐름을 변경하는 문장들.
- 조건문, 반복문, break, continue, return
*조건문 ( Conditional Statement)
-조건에 맞는 경우에만 코드를 실행해야할 때 사용하는 문장들.
-if, else, switch~case
*if)
- 단일 if, if~else, 다중 if( else~if) 세가지의 문법을 지원한다.
*단일 if : -조건에 맞는 경우에만 코드를 실행해야 할 때.
문법)
if( 조건식 ){
조건에 맞을 때 수행될 문장들,
....
}
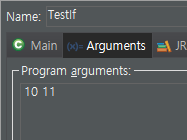
package day0117;
/**
* 단일 if 사용<br>
* if ( 조건식 ) { <br>
* 조건에 맞을 때 수행할 문장들...<br>
* }<br>
*
* 절대값을 구하는 코드를 작성.
*/
public class TestIf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int tempNum= -17;
int abs= tempNum;
if (tempNum < 0 ) { //음수이면
abs = -tempNum; //절대값으로
}//end if
System.out.println(tempNum +"의 절대값 " + abs +"입니다.");
int num=0;
num=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
if(num%2 == 0) {
System.out.println(num+"은(는)"+" 짝수입니다.");
}//end if
if(num%2 ==1 ) {
System.out.println(num+"은(는)"+" 홀수입니다.");
}//end if
if("Java".equals(args[0]) || "java".equals(args[0])) {
System.out.println("WORA, 완벽한 OOP언어, 메모리 관리의 편의성");
}//end if
//main method의 두번째 arguments에 (args[1]) 입력받은 값을 정수로 저장하여
//0~100사이인 경우에만 "xx점은 유효한 점수입니다."룰 콘솔에 출력하는 코드작성.
int score=Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
if (score>=0 && score<=100) {
System.out.println(score+"점은 유효한 점수입니다.");
}//end if
}//main
} //class
-17의 절대값 17입니다.
10은(는) 짝수입니다.
11점은 유효한 점수입니다.
*if~else
- 둘 중 하나의 코드를 실행해야 할 때.
문법)
if( 조건식 ){
조건에 맞을 때 수행될 문장들,,,,,,
}else{
조건에 맞지 않을 때 수행될 문장들,,,,,
}
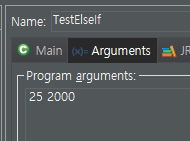
package day0117;
/**
* 다중 if : 연관된 여러 조건을 비교할 때 사용 <br>
* if (조건식) { <br>
* 조건에 맞을 때 수행될 문장들<br>
* }else if (조건식) { <br>
* 조건에 맞을 때 수행될 문장들 <br>
* }else if (조건식) { <br>
* 조건에 맞을 때 수행될 문장들 <br>
* }else
* 모든 조건에 맞지 않을 때 수행될 문장들
* }
*/
public class TestElseIf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//점수판별
//점수는 0보다 작을 수 없고, 100보다 클 수 없다.
//0보다 작은 경우 "0보다 작아서 실패"를 출력하고,
//100보다 크다면 "100보다 커서 실패"를 출력하고,
//그렇지 않다면 (0~100) "정상범위 점수"를 출력
int score = 100;
if (score<0) {
System.out.println("0보다 작아서 실패");
}else if (score>100) {
System.out.println("100보다 커서 실패");
}else
System.out.println("정상범위 점수");
//end else
//나이를 입력받아서 main method의 첫번째 arguments에 (args[0]) 나이를 입력받아서
//1~100살 사이일 때 9세까지는 어린이, 10대는 청소년, 그외에는 어른을 콘솔에 출력
//1~100살이 아니라면 "일반적인 나이가 아닙니다"를 출력하는 코드작성
int age = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
if (age<=9) {
System.out.println("당신은 "+age+"살이며, "+"어린이입니다.");
}else if (age<=19) {
System.out.println("당신은 "+age+"살이며, "+"청소년입니다.");
}else if (age<=100) {
System.out.println("당신은 "+age+"살이며, "+"어른입니다.");
}else
System.out.println("당신은 "+age+"살이며, "+"생존하셨습니다.");
//main method의 두번째 arguments에 (args[1]) 태어난해를 입력받아서
//나이와 띠를 콘솔에 출력하는 코드를 작성하세요.
//(0~11)원숭이-닭-개-돼지-쥐-소-호랑이-토끼-용-뱀-말-양
int birth = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int Year = 2025-birth+1; // 나이
if (birth % 12 == 0) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 원숭이띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 1) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 닭띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 2) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 개띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 3) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 돼지띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 4) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 쥐띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 5) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 소띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 6) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 호랑이띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 7) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 토끼띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 8) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 용띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 9) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 뱀띠");
}
else if (birth % 12 == 10) {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 말띠");
}
else {
System.out.println("태어난 해 : "+ birth+ " 나이는 : "+Year+ ", 양띠");
}
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
정상범위 점수
당신은 25살이며, 어른입니다.
태어난 해 : 2000 나이는 : 26, 용띠
*switch~case
- 일치하는 정수를 비교하기위해서 만들어진 조건문.
- Open JDK7( JDK1.7 ) 버전에서는 “문자열”을 비교할 수 있는 기능이 추가.
-동작 : 입력되는 변수와 일치하는 상수를 찾고, 그 아래 모든 case를 수행한다.
문법)
switch( 변수명 ){
case 상수 : 수행될 문장들….;
case 상수 : 수행될 문장들….; break;
.
.
default : 일치하는 상수가 없을 때 실행될 코드들…;
}
흐름)
int i=1;
switch( i ){
case 0 : System.out.println(“영”);
case 1 : System.out.println(“일”);
case 2 : System.out.println(“이”);
default : System.out.println(“해당케이스 없음.”);
}
*break
-switch~case, for, while문을 빠져나갈 때 사용하는 문장.
-Jump Statements ( break, continue, return )
- 특정 case만 실행하고 switch~case를 빠져 나가고 싶다.
int i=0;
switch( i ){
case 0 : System.out.println(“영”);
case 1 : System.out.println(“일”); break;
case 2 : System.out.println(“이”);
default : System.out.println(“해당케이스 없음.”);
}
*switch~case로 학점구하기 ( if 가 더 적절 )
A => 90~100
B => 80~89
C => 70~79
D => 60~69
F => 0~59
*looping Statements ( 반복문 )
- 코드를 여러 번 반복 실행해야 할 때.
- for, while, do~while
*for문)
-시작과 끝을 알때 사용.
-단일 for, 다중 for를 지원.
문법)
for( 초기값 ; 조건식 ; 증.감소식){
반복수행될 문장들….
}
package day0120;
/**
* switch ~ case 일치하는 정수를 비교할 때 사용하는 조건문
* switch (변수) {
* case 상수 : 변수값이 상수와 같을때 실행할 문장들,,,
* case 상수 : 변수값이 상수와 같을때 실행할 문장들,,,
*
* default : 변수값이 상수와 같은 값이 없을 때 실행할 문장들..
* }
*/
public class TestSwitchCase {
public static final int GRADE_A_PULS=10; //Constants 를 하면 좀더 가동성 있게 코딩 가능
public static final int GRADE_A=9;
public static final int GRADE_B=8;
public static final int GRADE_C=7;
public static final int GRADE_D=6;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int i = 1 ; //i 는 switch에 들어갈 변수
String i = "A"; // byte, short, int, char ,String(JDK1.7에서 추가)
switch (i) {
case "0": System.out.println("영");
case "1": System.out.println("일");
case "A": System.out.println("이");
case "3": System.out.println("삼");
default : System.out.println("변수와 일치하는 상수가 없다.");
}//end switch
System.out.println("-------------break-------------------");
int j = 0;
switch (j) {
case 0: System.out.println("영");
case 1: System.out.println("일");
case 2: System.out.println("이");
break;
case 3: System.out.println("삼");
default : System.out.println("변수와 일치하는 상수가 없다.");
}//end switch
System.out.println("-------------범위 비교-------------------");
//점수의 대학 학점 구하기
char grade = 'F';
int score = 100;
// if( score >= 0 && score <=100){ // 조건식 : 점수가 0~100사이라면
if( score > -1 && score <101){ // 조건식 : 점수가 0~100사이라면
switch (score/10) { // 범위
case TestSwitchCase.GRADE_A_PULS:
case TestSwitchCase.GRADE_A: grade = 'A'; break;
case TestSwitchCase.GRADE_B: grade = 'B'; break;
case TestSwitchCase.GRADE_C: grade = 'C'; break;
case TestSwitchCase.GRADE_D: grade = 'D'; break;
default : grade = 'F'; break;
}
System.out.println(score+ "점은"+grade+"학점입니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println(score+ "점은 잘못된 점수입니다.");
}//else end
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");
grade = 64;
score = 89;
if( score > -1 && score <101){ // 조건식 : 점수가 0~100사이라면
switch (score/10) { // 범위
case GRADE_D : grade++;
case GRADE_C : grade++;
case GRADE_B : grade++;
case GRADE_A :
case GRADE_A_PULS : grade++; break;
default : grade += 6;
}
System.out.println(score+ "점은"+grade+"학점입니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println(score+ "점은 잘못된 점수입니다.");
}//else end
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
이
삼
변수와 일치하는 상수가 없다.
-------------break-------------------
영
일
이
-------------범위 비교-------------------
100점은A학점입니다.
-----------------------------------------------------
89점은B학점입니다.
*다중 for
-for문안에 for문을 정의하는 것.
문법)
for( 초기값 ; 조건식 ; 증.감소식){
for(초기값 ; 조건식 ; 증.감소식) {
}
}

package day0120;
/**
* for : 시작과 끝을 알 때 사용하는 반복문<br>
* for(초기값 ; 조건식; 증.감소식){ <br>
* 반복수행 문장들.......<br>
*}
*/
public class TestFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i= 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
System.out.println("안녕하세요?" + i);
}//end for
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
//1에서 부터 100까지 1씩 증가하는 값을 옆으로 콘솔에 옆으로 출력해보세요.
for(int i= 1 ; i < 101 ; i++) {
System.out.print( i+" " );
}//end for
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
//1에서 부터 100까지 수중에 짝수만 콘솔에 옆으로 출력해보세요.
int cnt=0;
for(int i= 1 ; i < 101 ; i++ ) {
cnt++;
if(i %2 ==0) {
System.out.print(++ i+" " );
}
}//end for
System.out.println("\n"+cnt+"번 수행");
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
//1에서부터 100까지의 수중에 홀수만 콘솔에 옆으로 출력해보세요.
for(int i= 1 ; i < 101 ; i+=2/*++,--등 변수에 값을 변경하고 유지할 수 있는 연산자*/) {
// if(i %2 ==0) {
System.out.print( i + " " );
}//end for
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
//대문자를 모두 출력해보세요. A(65) B C.....Z(90)까지
for(int i=65; i <91; i++) {
System.out.print( (char)i + " " );
}//end for
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
for(char i='A'; i <='Z'; i++) {
System.out.print( i + " " );
}//end for
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
for(char i='A'; i <='Z'; i++) {
System.out.print( i +"("+(char)(i+32)+")");
}//end for
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
//1에서부터 100가지의 합 출력( 5050 )
int sum=0;
for(int i=1 ; i < 101 ; i++) {
sum += i;
}//end for
System.out.println("1에서부터 100까지의 합은:"+sum );
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
//구구단 2단 출력 2x1=2 2x2=4 아래로.
for(int i=1; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("2x" +i + " = " +2*i );
}//end for
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
//알파벳 Z~A까지 출력
char upper=65, lower=122;
for(char i=0; i<26; i++ ) {
System.out.print(upper++ + "( "+ lower-- +") "); // A(z) ,B(y), ,Z(a)
} //end for
System.out.println("\n-----------------------------------");
int multiplicationTable=0;
multiplicationTable=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
if(multiplicationTable > 1 && multiplicationTable <10) {
for (int i=1; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println(multiplicationTable + " X "+ i +
" = " + multiplicationTable*i );
}//end for
}//end if
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
안녕하세요?0
안녕하세요?1
안녕하세요?2
안녕하세요?3
안녕하세요?4
안녕하세요?5
안녕하세요?6
안녕하세요?7
안녕하세요?8
안녕하세요?9
------------------------------------------
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
-------------------------------------
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 101
51번 수행
-----------------------------------
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99
-----------------------------------
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
-----------------------------------
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
-----------------------------------
A(a)B(b)C(c)D(d)E(e)F(f)G(g)H(h)I(i)J(j)K(k)L(l)M(m)N(n)O(o)P(p)Q(q)R(r)S(s)T(t)U(u)V(v)W(w)X(x)Y(y)Z(z)
-----------------------------------
1에서부터 100까지의 합은:5050
-----------------------------------
2x1 = 2
2x2 = 4
2x3 = 6
2x4 = 8
2x5 = 10
2x6 = 12
2x7 = 14
2x8 = 16
2x9 = 18
-----------------------------------
A( z) B( y) C( x) D( w) E( v) F( u) G( t) H( s) I( r) J( q) K( p) L( o) M( n) N( m) O( l) P( k) Q( j) R( i) S( h) T( g) U( f) V( e) W( d) X( c) Y( b) Z( a)
-----------------------------------
2 X 1 = 2
2 X 2 = 4
2 X 3 = 6
2 X 4 = 8
2 X 5 = 10
2 X 6 = 12
2 X 7 = 14
2 X 8 = 16
2 X 9 = 18
*for문의 다양한 형태
-여러 개의 초기값을 가지는 for
주의 : 조건식은 하나만 설정.
for( 초기값,,,, ; 조건식 ; 증.감소식,,, ){
}
for( int i=0, j=10, k=100 ; i < 10 ; i++, j+=4; k-- ){
i, j, k
}
-무한루프( 종료되지 않아야하는 프로그램을 제작해야 할 때.)
문법)
-증가하는 수를 세는 무한 루프.
for( 초기값 ; ; 증.감소식){
}
-증가하는 수를 세지 않는 무한 루프.
for( ; ; ){
}
*무한루프 아래 라인에 코드를 정의하면, 해당코드는 실행될 수 없기 때문에 에러가 발생.
*continue
- 반복문안에서 반복문의 실행을 건너 뛰는 일.( 반복실행을 건너뛰고 증. 감소식으로 이동)
- 반복문안에서 조건문 사용하여 비교하고 반복수행 문장을 건너뛰게 만든다.
사용법)
for(초기값 ; 조건식; 증.감소식){
필수 반복수행문장 들…
if( 조건식 ){
continue;
}
선택 반복수행문장 들…
}
*while
-시작과 끝을 모를 때 사용하는 반복문.
-최소 0번 수행 최대 조건까지 수행.
문법)
초기값;
while( 조건식 ){
반복수행문장,,,,;
증.감소식;
}
package day0121;
/**
* while : 시작과 끝을 모를 때 사용하는 반복문 <br>
* 최소 0번 수행, 최대 조건까지 수행<br>
* while( 조건식 ) { <br>
* 반복수행문장틀 <br>
* 증.감소식 <br>
* }
*/
public class TestWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=0;
while( i < 10 ) {
System.out.println("i = "+ i );
i++;
}//end while
//while을 사용하여 1~100사이에 3의 배수 합을 구하여 출력하세요.
int sum=0;
i=1;
while( i < 101) {
if(i % 3 == 0) {
sum+= 1;
}//end if
i++;
}//end while
System.out.println(sum);
//while의 무한 루프
while (true) {
System.out.println("무한루프");
break;
}//end while
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
i = 0
i = 1
i = 2
i = 3
i = 4
i = 5
i = 6
i = 7
i = 8
i = 9
33
무한루프
*do~while
-시작과 끝을 모를 때 사용하는 반복문.
-최소 1번 수행에 최대 조건까지 수행.
문법)
초기값;
do{
반복수행문장들,,,,, ;
증.감소식;
}while( 조건식 );
package day0121;
/**
* do~while : 최소 1번 수행, 최대 조건까지 수행 <br>
* 초기값; <br>
* do { <br>
* 반복수행문장들... ; <br>
* 증.감소식; <br>
* } while ( 조건식 ) ; <br>
*/
public class TestDoWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int i = 100;
//
// do {
// System.out.println("i = " + i);
// i++;
// }while ( i <10 );
//
//do~while : 구구단 5단만 출려
int i = 5;
int j = 1;
do {
System.out.println(i +" * " + j + " = "+ i*j);
j++;
} while ( j<10 );
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
5 * 1 = 5
5 * 2 = 10
5 * 3 = 15
5 * 4 = 20
5 * 5 = 25
5 * 6 = 30
5 * 7 = 35
5 * 8 = 40
5 * 9 = 45
*Variable ( 변수 )
- 프로그램에서 필요한 값을 일시적으로 저장하고 사용하기 위해.
- 가독성향상.
- 선언하는 영역에따라 instance variable, static variable, local variable 3가지로 구분.
*static(class) variable –공용변수 ( 하나의 변수가 만들어지고 사용된다.)
- class field에 정의.
- 객체화 없이 클래스명으로 사용할 수 있다.( 클래스명.변수명 )
- 자동초기화가 된다.
- default value => 변수 선언 후 자동으로 정해진 값이 들어가므로
바로 사용하더라도 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
- 클래스가 실행되면 메모리에 올라가고, 프로그램이 종료되면 메모리에서 내려온다.
- 참조하는 속도가 빠르다.
- 메모리의 사용을 절감 할 수 있다.
문법)
1.선언)
접근지정자 static 데이터형 변수명;
2.값 할당) => 객체화 없이 바로 사용가능
클래스명.변수명=값;
3.값 사용)
클래스명.변수명
*instance(member) variable
- 특정 객체마다 생성되고, 사용되는 변수.
- class field에 정의한다.
- 자동초기화가 된다. ( default value 할당 )
- instance 를 생성한 후 ( 객체화 후 ) “객체명.변수명”으로 사용한다.
- 객체 생성될 때 메모리에 올라가고, 객체가 소멸되면 메모리에서 내려온다.
- 생성된 객체마다 같은 이름의 변수를 멤버로 가지고 있다.
사용법)
1.선언) –class field
접근지정자 데이터형 변수명;
package day0121;
/**
* instance(member) variable 사용<br>
* -객체마다 생성되고 사용되는 변수<br>
* 객체화 후 객체명.변수명으로 사용<br>
* 객체마다 같은 이름의 변수가 생성
*/
public class UseInstanceVariable {
public int i;
public void temp() {
i=100;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//2. static 영역에서 instance 변수를 사용하기 위해 객체화가 선행되어야 함
//객체화의 문법 : 클래스명 객체명=new 클래스명();
UseInstanceVariable uiv=new UseInstanceVariable(); //uiv라는 객체 생성
UseInstanceVariable uiv2=new UseInstanceVariable(); //uiv2라는 객체 생성
//3. 값 할당) 객체명.변수명=값
uiv.i=10; //객체(uiv)마다 같은 이름의 변수(i)가 존재
uiv2.i=21; //객체(uiv2)마다 같은 이름의 변수(i)가 존재
//4. 값 사용) 객체명.변수명
System.out.println("uiv객체 i 변수 : " + uiv.i);
System.out.println("uiv2객체 i 변수 : " + uiv2.i);
}//main
}//class
콘솔 출력
uiv객체 i 변수 : 10
uiv2객체 i 변수 : 21
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] Array,Variable Array (0) | 2025.03.16 |
|---|---|
| [Java] Method Overroad, this (0) | 2025.03.14 |
| [Java] Method - Instance ,Static,Variable 및 4가지 형태 (0) | 2025.03.13 |
| [Java] 이클립스 자바 코딩 연습(기본 문법,데이터 형,최대,최소,연산자) (0) | 2025.01.29 |
| 근성 개발자 성장 스토리 (0) | 2025.01.29 |
